Share this
Mini Guide on Low Latency
by THEO Technologies on May 11, 2021
When it comes to live video, it's hard to deliver an actual, real live streaming experience. The latency problem is especially noticeable when video is distributed using online streaming platforms. You may have heard the stories of watching a sports event and hearing the neighbours cheer, before seeing the start of an attack. In this mini guide, we'll present the five things you should know about low latency.
.png?width=680&height=355&name=A%20comprehensive%20Guide%20to%20Low%20Latency%20(3).png)
1) WHAT IS LATENCY?
Within a streaming environment, latency is most easily experienced by measuring the time when something is recorded in real life and when it is seen on the screen, for example waving your hand in front of a camera and watching it move on the screen a certain time later.
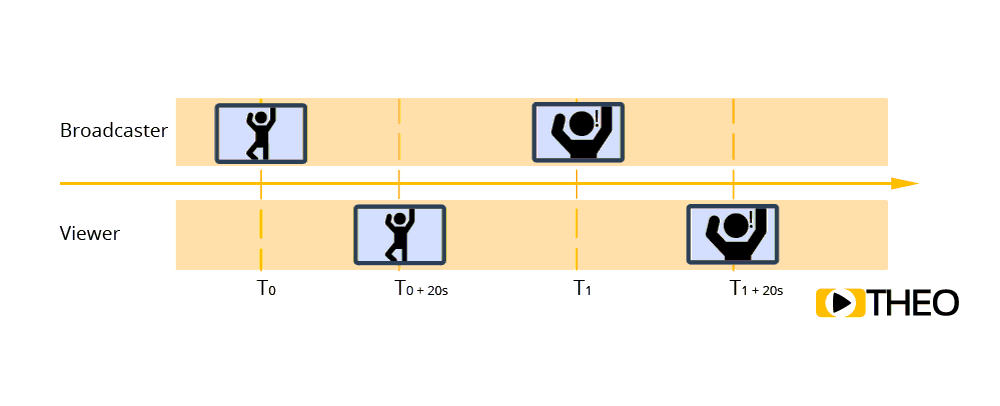
Having a high latency on streams, and especially in interactive live experiences, can have a significant impact on user experience. Imagine a live stream with a latency of about 20s with an interactive chat box where the audience can ask questions:
this would mean the person starring in the video could perform some action at a certain time T0. This image would show up on viewers’ screens 20s later.
"Latency is often described as "the time between cause and effect of some physical change"."
During this time, the broadcaster would simply continue with whatever he is doing. However, if a user would then type in and ask a question about the action at T0, showing up on the broadcaster’s screen, the broadcaster might be doing something completely different already, and have lost context. In return a (wrong) answer would still take another 20s before the answer gets back to the viewer!
2) WHAT CAUSES LATENCY?
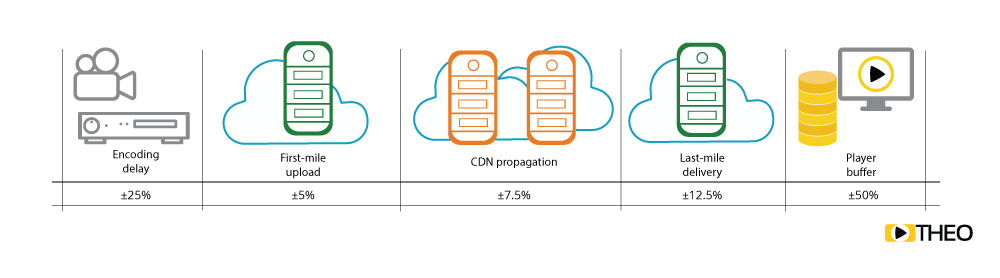
- Encoding & packaging: Latency introduced is very sensitive to the configuration and quality of the output signal needed to be achieved. Certain streaming protocols can introduce additional latency, as they can only output a chunk of media once it has been completely ingested.
- First mile upload: Uploading the packaged content to a CDN is often restrained by the business case. For example, an upload will have a significantly larger impact if done over a wireless connection at an event, compared to a leased line setup coming from a news studio.
- CDN propagation: In order to deliver content at scale, most media pipelines leverage content delivery networks. As a result, content needs to propagate between different caches, introducing additional latency.
- Last mile delivery: A user's network connection can have a significant impact on latency. The user could be on a cabled network at home, be connected to a wifi hotspot, or using amobile connection in order to access the content. Also, depending on geographical location and position of the closest CDN endpoint, additional latency could be added.
- Player buffer: Video players have to buffer media in order to ensure smooth playback. Often the sizes of buffers are defined in media specifications, but in some cases there is some flexibility in this area. Also, optimising buffer configuration can go a long way given the significant impact of this component.
-png.png?width=464&height=242&name=EZDRM%20blog%20banner%20(12)-png.png)
3) LATENCY VS SCALABILITY VS QUALITY
.png?width=477&height=249&name=EZDRM%20blog%20banner%20(13).png)
LATENCY <> SCALABILITY <> QUALITY
When looking at latency, we must also consider two other key factors at play: scalabilty and quality.
SCALE
In the past, streaming protocols were severely limited in their scalability. However, streaming protocols such as HTTP Live Streaming (HLS) and MPEGDASH make use of HTTP, and as a result can use standard HTTP caches and CDNs in order to scale. A downside of these protocols however, is that scalability is traded for latency.
QUALITY
Achieving a higher quality for the enduser often results in higher bandwidth requirements. Due to higher resolutions and frame rates, or more time needed on the encoder side in order to shrink the bitstream at high quality.
BALANCE
While new technology and compression algorithms will shift the achieved results, and make lower latency more achievable, finding the right balance within this latency trade off triangle will always be important. Impact of technological improvements can already be seen in the advances made by cloud computing, which significantly reduced scaling challenges as well as new media codecs such as VP9, HEVC and AV1. Reducing the required bandwidth significantly, compared to older techniques.
4) LATENCY INDUSTRY STANDARDS
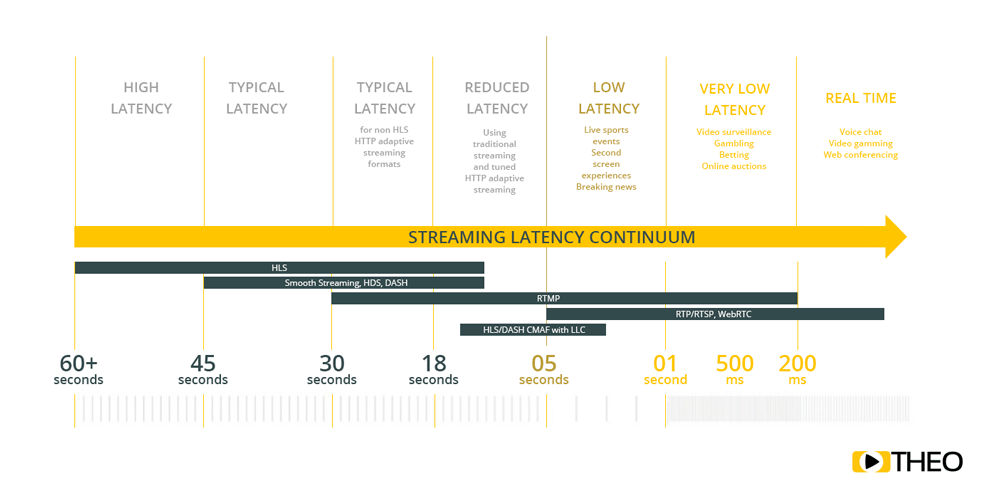
While optimising latency is surely important, a question we often get is “How low should your latency be?”. The answer will depend on the business case. In general, we advise our customers to make a number of changes to reduce latency already to be within the 18-30s range. This can be achieved with minimal effort and cost.
In contrast to regular broadcasting, for a real live show, the delay from the actual events to the moment it gets shown on a television set, today, is something between 4 -10s. Significantly lower than the industry standard protocols HLS & DASH as shown in the image.
When latencies comparable to broadcasting are to be achieved, it is interesting to have a look at recent advancements in protocols such as the newer Low Latency CMAF of Chunked CMAF standards being implemented by vendors.
"Regular broadcasting latency is still significantly lower than the default OTT latencies of 18-30s"
In the instance that a business case requires ultra low latency, or real time latency, solutions such as RTMP or WebRTC are required. This results in high costs when scaling and increasing quality.
.png?width=464&height=242&name=EZDRM%20blog%20banner%20(14).png)
5) WHEN IS LOW LATENCY IMPORTANT?
Obviously no one benefits from very high latencies. However, there are a number of cases where low latencies, even below broadcast latencies, are required.
Second screen experience: when watching a television show in parallel with regular broadcast, latencies preferably match at least the latency of the broadcast itself. Furthermore, every form of interactivity require the latencies to be synced as much as possible.
Live sports, E-sports and video game streaming: timing in live events, especially if the audience interacts with the live events which is becoming more frequent, reaching live latencies is becoming crucial.
Video Chat: this is where real-time latencies come in to play. Everyone knows the case where a live journalist is interviewed by the news anchor at a distant location. It takes several seconds before the correspondent can respond to the anchor's question. This negatively impacts the user experience.
Any questions left? Contact our THEO experts.
Share this
- THEOplayer (46)
- online streaming (40)
- live streaming (35)
- low latency (32)
- video streaming (32)
- HESP (24)
- HLS (21)
- new features (21)
- THEO Technologies (20)
- SDK (19)
- THEOlive (17)
- best video player (17)
- cross-platform (16)
- html5 player (16)
- LL-HLS (15)
- online video (15)
- SmartTV (12)
- delivering content (12)
- MPEG-DASH (11)
- Tizen (11)
- latency (11)
- partnership (11)
- Samsung (10)
- awards (10)
- content monetisation (10)
- innovation (10)
- Big Screen (9)
- CDN (9)
- High Efficiency Streaming Protocol (9)
- fast zapping (9)
- video codec (9)
- SSAI (8)
- Ultra Low Latency (8)
- WebOS (8)
- advertising (8)
- viewers expercience (8)
- "content delivery" (7)
- Adobe flash (7)
- LG (7)
- Online Advertising (7)
- Streaming Media Readers' Choice Awards (7)
- html5 (7)
- low bandwidth (7)
- Apple (6)
- CMAF (6)
- Efficiency (6)
- Events (6)
- drm (6)
- interactive video (6)
- sports streaming (6)
- video content (6)
- viewer experience (6)
- ABR (5)
- Bandwidth Usage (5)
- Deloitte (5)
- HTTP (5)
- ad revenue (5)
- adaptive bitrate (5)
- nomination (5)
- reduce buffering (5)
- release (5)
- roku (5)
- sports betting (5)
- video monetization (5)
- AV1 (4)
- DVR (4)
- Encoding (4)
- THEO Technologies Partner Success Team (4)
- Update (4)
- case study (4)
- client-side ad insertion (4)
- content encryption (4)
- content protection (4)
- fast 50 (4)
- google (4)
- monetization (4)
- nab show (4)
- streaming media west (4)
- support matrix (4)
- AES-128 (3)
- Chrome (3)
- Cost Efficient (3)
- H.265 (3)
- HESP Alliance (3)
- HEVC (3)
- IBC (3)
- IBC trade show (3)
- React Native SDK (3)
- THEOplayer Partner Success Team (3)
- VMAP (3)
- VOD (3)
- Year Award (3)
- content integration (3)
- customer case (3)
- customise feature (3)
- dynamic ad insertion (3)
- scalable (3)
- server-side ad insertion (3)
- video (3)
- video trends (3)
- webRTC (3)
- "network api" (2)
- Amino Technologies (2)
- Android TV (2)
- CSI Awards (2)
- Encryption (2)
- FireTV (2)
- H.264 (2)
- LHLS (2)
- LL-DASH (2)
- MPEG (2)
- Microsoft Silverlight (2)
- NAB (2)
- OMID (2)
- Press Release (2)
- React Native (2)
- Start-Up Times (2)
- UI (2)
- VAST (2)
- VP9 (2)
- VPAID (2)
- VPAID2.0 (2)
- ad block detection (2)
- ad blocking (2)
- adobe (2)
- ads in HTML5 (2)
- analytics (2)
- android (2)
- captions (2)
- chromecast (2)
- chromecast support (2)
- clipping (2)
- closed captions (2)
- deloitte rising star (2)
- fast500 (2)
- frame accurate clipping (2)
- frame accurate seeking (2)
- metadata (2)
- multiple audio (2)
- playback speed (2)
- plugin-free (2)
- pricing (2)
- seamless transition (2)
- server-side ad replacement (2)
- subtitles (2)
- video publishers (2)
- viewer engagement (2)
- wowza (2)
- "smooth playback" (1)
- 360 Video (1)
- AOM (1)
- API (1)
- BVE (1)
- Best of Show (1)
- CEA-608 (1)
- CEA-708 (1)
- CORS (1)
- DIY (1)
- Edge (1)
- FCC (1)
- HLS stream (1)
- Hudl (1)
- LCEVC (1)
- Microsoft Azure Media Services (1)
- Monoscopic (1)
- NAB Show 2016 (1)
- NPM (1)
- NetOn.Live (1)
- OTT (1)
- Periscope (1)
- Real-time (1)
- SGAI (1)
- SIMID (1)
- Scale Up of the Year award (1)
- Seeking (1)
- Stereoscopic (1)
- Swisscom (1)
- TVB Europe (1)
- Tech Startup Day (1)
- Telenet (1)
- Uncategorized (1)
- University of Manitoba (1)
- User Interface (1)
- VR (1)
- VR180 (1)
- Vivaldi support (1)
- Vualto (1)
- adblock detection (1)
- apple tv (1)
- audio (1)
- autoplay (1)
- cloud (1)
- company news (1)
- facebook html5 (1)
- faster ABR (1)
- fmp4 (1)
- hiring (1)
- iGameMedia (1)
- iOS (1)
- iOS SDK (1)
- iPadOS (1)
- id3 (1)
- language localisation (1)
- micro moments (1)
- mobile ad (1)
- nagasoft (1)
- new web browser (1)
- offline playback (1)
- preloading (1)
- program-date-time (1)
- server-guided ad insertion (1)
- stream problems (1)
- streaming media east (1)
- support organization (1)
- thumbnails (1)
- use case (1)
- video clipping (1)
- video recording (1)
- video trends in 2016 (1)
- visibility (1)
- vulnerabilities (1)
- zero-day exploit (1)
- November 2024 (1)
- August 2024 (1)
- July 2024 (1)
- January 2024 (1)
- December 2023 (2)
- September 2023 (1)
- July 2023 (2)
- June 2023 (1)
- April 2023 (4)
- March 2023 (2)
- December 2022 (1)
- September 2022 (4)
- July 2022 (2)
- June 2022 (3)
- April 2022 (3)
- March 2022 (1)
- February 2022 (1)
- January 2022 (1)
- November 2021 (1)
- October 2021 (3)
- September 2021 (3)
- August 2021 (1)
- July 2021 (1)
- June 2021 (1)
- May 2021 (8)
- April 2021 (4)
- March 2021 (6)
- February 2021 (10)
- January 2021 (4)
- December 2020 (1)
- November 2020 (1)
- October 2020 (1)
- September 2020 (3)
- August 2020 (1)
- July 2020 (3)
- June 2020 (3)
- May 2020 (1)
- April 2020 (3)
- March 2020 (4)
- February 2020 (1)
- January 2020 (3)
- December 2019 (4)
- November 2019 (4)
- October 2019 (1)
- September 2019 (4)
- August 2019 (2)
- June 2019 (1)
- December 2018 (1)
- November 2018 (3)
- October 2018 (1)
- August 2018 (4)
- July 2018 (2)
- June 2018 (2)
- April 2018 (1)
- March 2018 (3)
- February 2018 (2)
- January 2018 (2)
- December 2017 (1)
- November 2017 (1)
- October 2017 (1)
- September 2017 (2)
- August 2017 (3)
- May 2017 (3)
- April 2017 (1)
- March 2017 (1)
- February 2017 (1)
- December 2016 (1)
- November 2016 (3)
- October 2016 (2)
- September 2016 (4)
- August 2016 (3)
- July 2016 (1)
- May 2016 (2)
- April 2016 (4)
- March 2016 (2)
- February 2016 (4)
- January 2016 (2)
- December 2015 (1)
- November 2015 (2)
- October 2015 (5)
- August 2015 (3)
- July 2015 (1)
- May 2015 (1)
- March 2015 (2)
- January 2015 (2)
- September 2014 (1)
- August 2014 (1)